Tulsa has a rich historical legacy and a commitment to fostering growth and equity. Known for its resilience and forward-thinking leadership, Tulsa is home to over 413,000 residents and continues to evolve as a center for innovation, education, and economic opportunity. As of the 2020 US Census, Tulsa’s population comprised primarily 48.5% White, 19.1% Hispanic or Latino, 14.6% Black, and 4.6% Native American or Alaska Native.

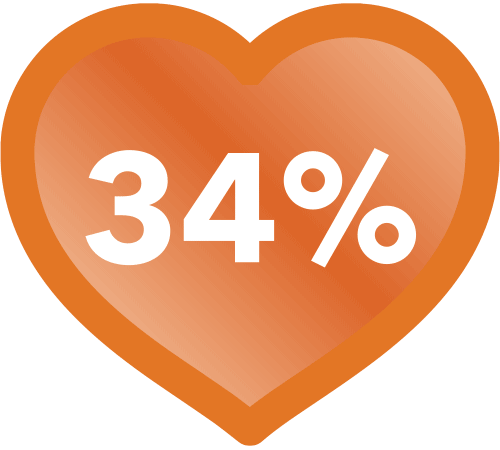
of supports measured
The city was also the site of the Tulsa Massacre in 1921, in which mobs of white residents attacked and killed Black residents and destroyed their homes and businesses, leaving the vibrant Black community once called “Black Wall Street” in ruins, a crime and disaster from which it has taken generations to recover.
Previously known for its oil industry, Tulsa has diversified its economy and transitioned into a center for aerospace, advanced manufacturing, healthcare, and technology. This economic transformation is supported by strategic programs like Tulsa Remote, which attracts remote workers, and A Better Way, which connects individuals experiencing homelessness with job opportunities. In the education sector, ImpactTulsa unites schools, nonprofits, and community leaders to improve student outcomes, ensuring children have the opportunity to succeed.
Tulsa has made significant strides in advancing education, economic stability, and public health, setting the stage for a more inclusive and prosperous community. The city’s leadership is dedicated to reducing disparities and increasing access to opportunities through innovative programs and policies.
Expand to read more
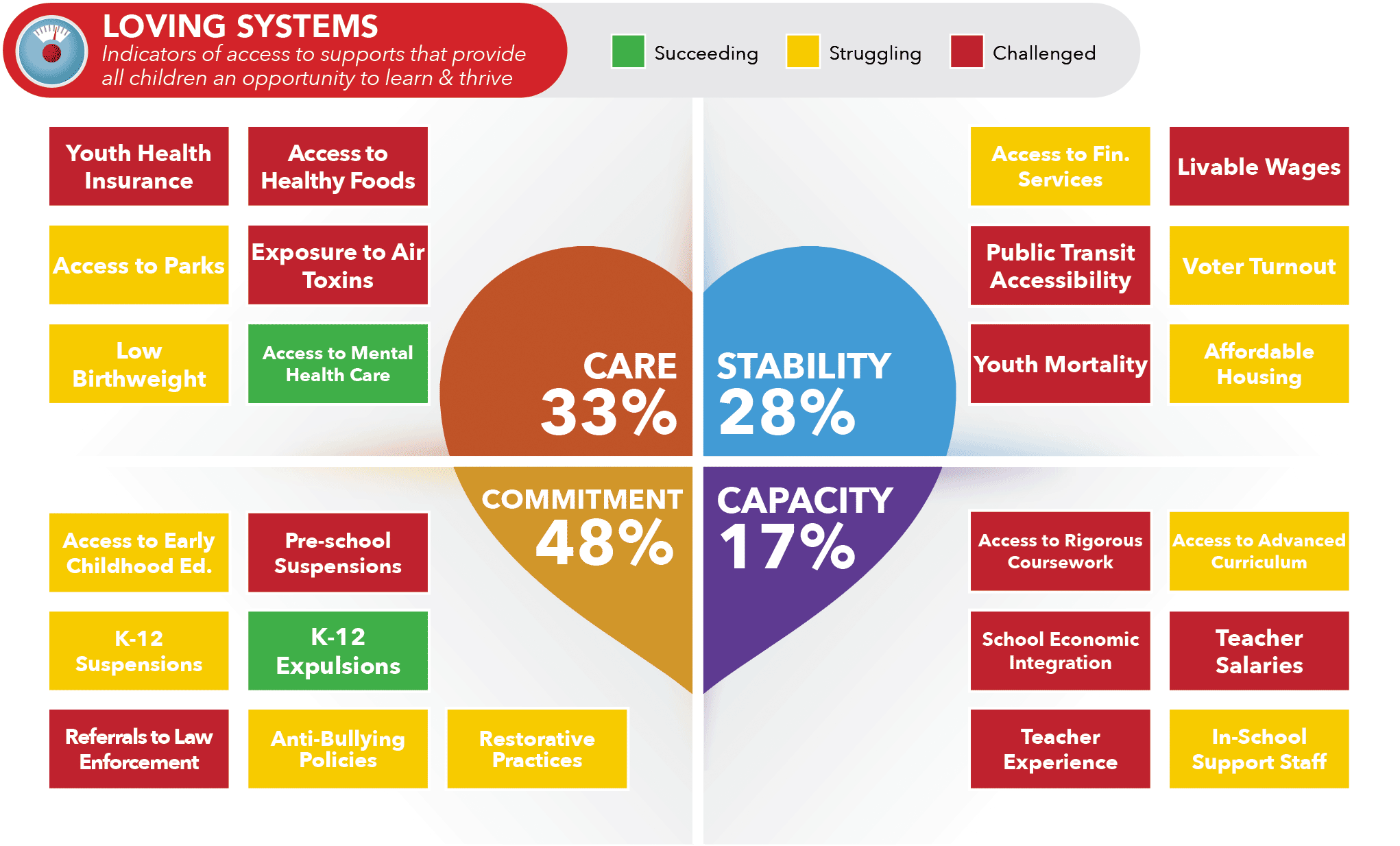
Education remains a priority. The Birth through Eight Strategy for Tulsa (BEST) program, a collaboration between local and national partners, focuses on early childhood development, ensuring young learners have access to quality education from the start. Tulsa is expanding access to rigorous coursework through Tulsa Public Schools’ College and Career Readiness program, which provides AP, IB, and dual enrollment opportunities.
Economic mobility is strengthened through initiatives such as Tulsa’s Economic Empowerment Program (TEEM), which helps individuals re-enter the workforce after incarceration, and Tulsa Responds, which provides financial literacy and tax assistance to low-income families. While Tulsa has a robust financial services sector, many working-age residents still earn below a livable wage, and transit accessibility remains a barrier for some households. Expanding transportation options and job training programs will strengthen economic stability.
Tulsa has also made meaningful progress in health and wellness. The Tulsa Health Department’s Pathways to Health initiative focuses on expanding healthcare access and reducing health disparities, but the trend of “pharmacy deserts” is a growing concern. The city has strong youth health insurance coverage and well-maintained parks, but air quality concerns and limited mental health resources present areas for improvement. Investments in green infrastructure and mental health care will enhance overall well-being.
By focusing on these key areas, Tulsa is positioning itself as a city that prioritizes opportunity, inclusion, and long-term prosperity for all its residents.
Tulsa Indicators
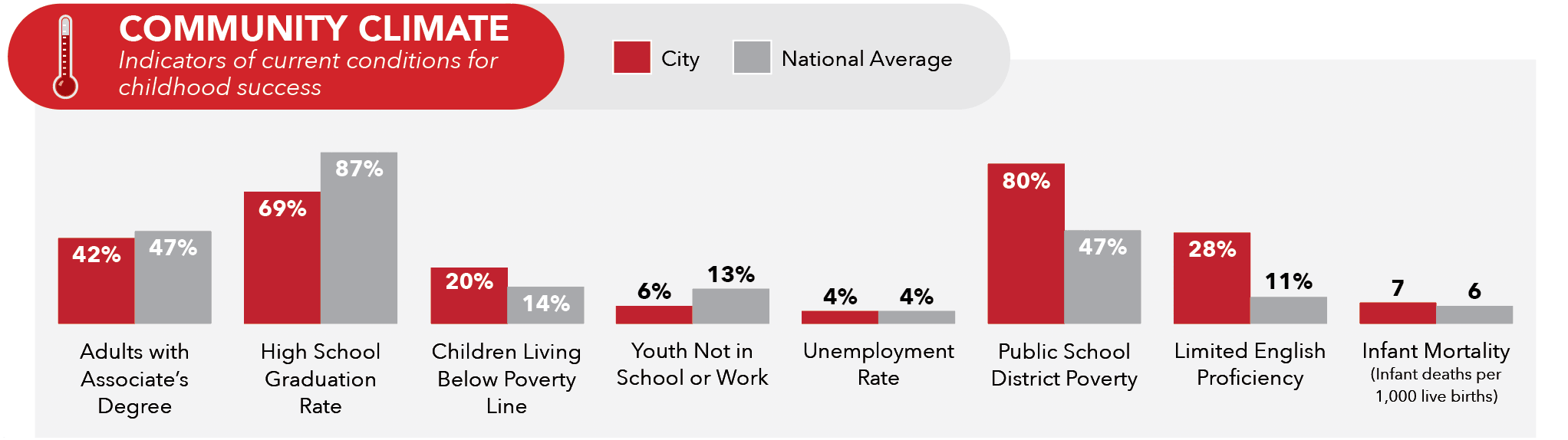
The Community Climate comprises indicators of a city’s current conditions in important areas such as education, economic stability, and public health. While these indicators do not uncover underlying supports or influences in a city, the outcomes provide a picture of a community’s well-being, economic mobility, and equitable opportunities.